CISSP Series Domain3 Episode 24 - Cryptography 1000ft overview
Welcome back!!!
It’s been a while since our last episode in the CISSP series, but I'm thrilled to dive back into the fascinating world of information security with you all. Apologies for the delay; life has a way of keeping us on our toes, doesn't it? But here we are, ready to unravel the mysteries of cryptography, a topic close to my heart and a driving force behind my journey into the realm of information security.
Understanding Cryptography and Cryptology:
Let's begin with the basics. Cryptology, the science of encryption and decryption, forms the backbone of secure communication in the digital age. Within cryptology, we encounter two distinct branches: cryptography and cryptanalysis.
Cryptography: The art of encoding messages, ensuring that only authorized individuals can decipher them.
Cryptanalysis: The counterpart to cryptography, involving the deciphering of encrypted messages through various methods and techniques.
Exploring Encryption Techniques:
At the core of cryptography lies the transformation of plaintext into ciphertext, a process essential for safeguarding sensitive information. We employ two primary techniques for this transformation:
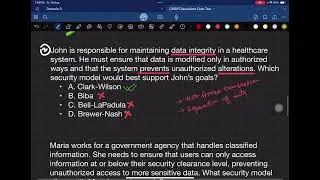
1. Substitution Technique: Here, characters in the message are replaced with alternate characters, adding a layer of complexity to the encoded text. The infamous Caesar Cipher exemplifies this method.
2. Transposition Technique: Unlike substitution, transposition involves rearranging the order of characters within the message, often through permutation or other manipulations. Techniques like the Vernam Cipher and rail-fence cipher fall under this category.
While delving into these techniques' intricacies is fascinating, it's important to maintain a high-level understanding, especially for CISSP exam purposes.
Navigating Cryptographic Techniques:
As we venture deeper, we encounter two fundamental cryptographic techniques:
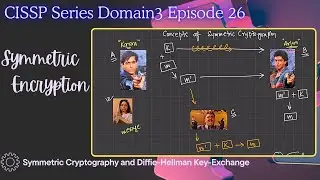
Symmetric Key Cryptography: Employing a single key for both encryption and decryption, this method simplifies the process while maintaining security.
Asymmetric Key Cryptography: Utilizing a pair of keys – public and private – for encryption and decryption, respectively, this technique offers enhanced security through key distribution.
Understanding these techniques lays the groundwork for comprehending the nuances of encryption and decryption mechanisms.
Algorithm Types and Modes:
Within symmetric key cryptography, algorithm types and modes play crucial roles in defining encryption processes.
Algorithm Type: Determines the input size of the message, whether it's processed as a stream or block cipher.
Algorithm Mode: Specifies the details of the cryptographic algorithm, such as encryption mechanisms and block processing.
Exploring modes like Electronic Code Book (ECB), Cipher Block Chaining (CBC), Cipher Feedback (CFB), Output Feedback (OFB), and Counter Mode provides insight into the diverse encryption methodologies employed in information security.
Linking Cryptography to Information Security Principles:
As we journey through the realm of cryptography, it's vital to remember its broader implications for information security. The six fundamental principles – confidentiality, integrity, authenticity, non-repudiation, access control, and availability – serve as guiding beacons, shaping our approach to securing digital assets.
Thank you for embarking on this cryptographic expedition with me! While our upcoming videos may adopt a more verbal format, rest assured, the passion for sharing knowledge remains undiminished. Don't forget to like, subscribe, and share your thoughts in the comments below. Together, let's continue unraveling the mysteries of information security, one episode at a time.
Until next time, stay curious, stay secure!
#CISSP #CCSP #nist