MPEG 4 vs H.264 Difference Explained for Beginners: Which to Choose for Your Video Project?
0:00 Introduction - MPEG 4 vs H.264 Difference Explained
0:52 MPEG-4 Explained
1:05 MPEG-4 Extensions
1:37 H.264 Explained
2:32 Where is H.264 Used
This video explains MPEG-4 vs H.264 Difference.
MPEG 4 and H.264 are codecs used to compress video files.
Are you wondering which of the two to choose for your video project?
If so, this video will educate you about the differences between the two formats to help you make the right decision.
Understanding these differences can help you choose the right format for your needs, whether you're streaming video online, recording high-definition content, or distributing media on physical discs.
Let's first start with MPEG 4.
The MPEG 4 codec has been around since 1999.
When it was first developed, it was meant to be used for Internet video streaming.
It is also suitable for video playback on portable devices like mobile phones.
MPEG 4 files have extensions like .mp4, .m4a, and .m4b.
.m4a is used for audio, and .m4b is used for audiobooks.
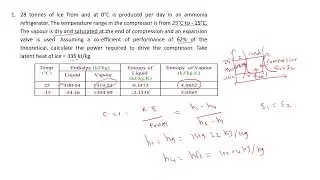
The main advantage of MPEG 4 is video can be compressed to smaller sizes.
To get smaller file sizes, a lower bitrate has to be used. This results in lower video quality.
Quality loss isn't noticeable on smaller screens like on mobile phones.
However, it's noticeable on larger TV screens.
H.264 is a popular codec as it encodes high-quality images without taking up much bandwidth.
Its licensing fees are more affordable for software developers and hardware manufacturers.
H.264 is actually MPEG 4 part 10. Although a part of MPEG 4, it is a more advanced and specific video compression standard.
It was designed for high compression efficiency and video quality.
H.264 is also known as AVC or Advanced Video Coding.
However, industry circles call it H 264 to differentiate it.
H.264 is a versatile codec that supports both streaming and high-definition videos, ranging from 4K to 8K.
Most video cards have H.264 encoding, decoding, and transcoding capabilities.
Web browsers also offer support for the H.264 codec.
H.264 is widely used in Blu-ray discs, online streaming services (like YouTube and Netflix), and digital television broadcasting.
It's also popular for video conferencing and recording.
In summary, MPEG 4 is a versatile standard for various types of multimedia content but is less efficient in video compression than H.264.
H.264 is a more advanced standard focused on high-quality video compression, widely used for HD content and online streaming.
Now that you know the difference between MPEG-4 and H.264, we hope you can decide which to choose for your video project.