Transistor used as temperature sensor, how to make that work: demo & schematic (Germanium-Silicium)
Please read the description/textbox first.
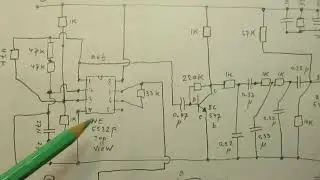
The video shows 2 (two) basics schematics about how to use a Silicon transistor or a Germanium transistor as a temperature sensor.
The choice of the transistors is not very critical.
Because how it works (how the temp. is reigned in both cases: via the GE or SI voltage drop) depends for the biggest part on the physics properties of the Germanium and Silicon material.
This means that you can use in practice “every” universal Germanium transistor or universal Silicon transistor to do this job, as long as they are “bare”.
Thus usable for a thermometer, or to switch something “on” or “off” when the temperature gets too high or too low.
Can be done with a Comparator (say a 741 or a TL 071) or better (more precise) a 3 transistor Schmitt trigger circuit that can switch within 1/10 or even 1/100 of a Volt, related to the temperature.
You can search that via my channel trailer “Radiofun232 on You Tube” and then via the “looking glass” and keywords to find more circuits regarding the Schmitt Trigger, Comparators, etc.
Search terms “Schmitt trigger” or “Comparator”.
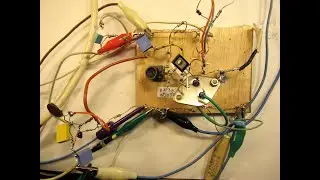
The demo shows the fierce voltage change/drop, when the Germanium transistor sensor (AC 187 in that copper pipe) is dipped into hot and cold water. Changing voltages in the (+) range, easy to use in a comparator circuit.
I did not demonstrate the Silicium-transistor temperature sensor, but that works in the 0 Volt (+) to 1 Volt (+), you can also drive a Comparator (TL071 or a 741 Opamp) with/via the changes of that (small) voltage, when it changes due to the warming up of that Silicon transistor.
CORRECTIONS and remarks to the video:
6.37-6.38 I am talking about the use of NPN Germanium transistors (given the schematic in the video)
9.23: shift/move the “how to” picture somewhat about how to solder everything in (referred to the schematic)
The “take voltage out” in the schematics go to the wiper(s) of the 470 K potentiometers. There the voltage goes up/down, related to the temperature of the transistor(s).
Via a series resistor (say 1 K) you can lead that changing voltage e.g. to a Comparator with a 741 or a TL 071 or another Schmitt trigger.
Via the output of that Comparator/Schmitt trigger you can activate a relay, or whatever.
More info in old video’s on my YT Channel (to be found via keywords like “Schmitt Trigger” or “Comparator” or “switch”).
More video’s to come, the aim of all this is to make a water bath on 38 Degrees Celsius for photographic (color dia film reversal development) purposes.
There are, of course, many parameters to make such a temperature (38 degrees Celsius) stable water bath, anyway. Not only about electronics, but also the heater element, the precise switching on-off, the loss of temperature in the bath (quick-slow), how good the electronics can drive this, etc.
My You Tube channel trailer is here: • Radiofun232 on YouTube. Updated monthly.
When you search, search always “NEWEST FIRST” to get the right overview. You can also search via the “looking glass” on my Channel trailer via keywords like ”audio”, “radio”, “amplifier”, “filter”, “Shortwave”, “transistor”, “FET”, “oscillator”, “generator”, “switch”, “schmitt trigger” etc; so the electronic subject you are interested in.
My books about electronics & analog radio technology are available via the website of "LULU”, search for author “Ko Tilman” there.
https://www.lulu.com/search?adult_aud...
I keep all my YT videos constant actual, so the original video’s with the most recent information are always on YouTube. Search there, and avoid my circuits that are republished, re-arranged, re-edited on other websites, giving not probable re-wiring, etc. Some persons try to find gold via my circuits. I take distance from all these (fake) claims. I cannot help that these things happen. Upload 24 April 2023.