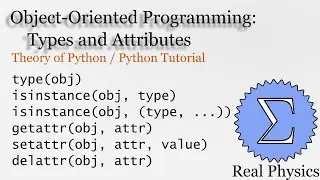
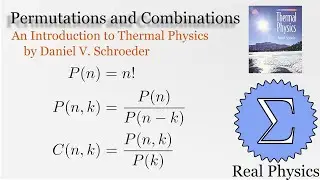
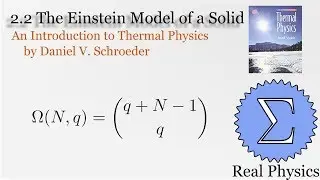
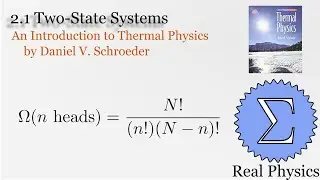
1.7 Rates of Processes: Conductivity of an Ideal Gas (Thermal Physics) (Schroeder)
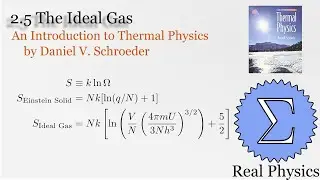
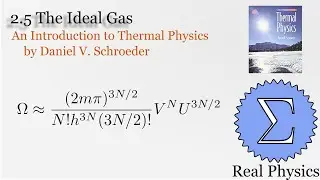
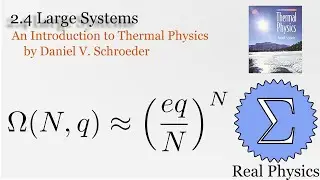
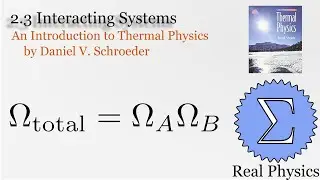
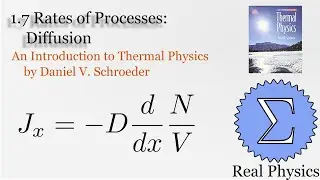
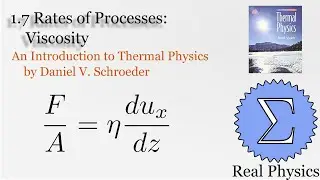
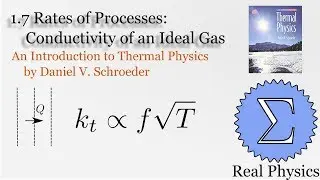
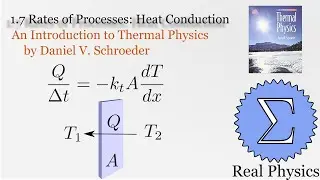
Assuming an ideal gas, we can do some simple calculations to obtain the mean free path of a molecule of that gas, and then given the root mean square of the velocity, the average time between collisions. Using a simple thought experiment of dividing up a gas with a temperature gradient, we can calculate the coefficient of heat conductivity of the gas, which aligns reasonably well with measured values. This technique is another example of kinetic theory. Using kinetic theory, we can determine how substances behave outside of the equilibria which thermodynamics is good at investigating.
Playlist: • An Introduction to Thermal Physics by...
Join us on Discord: / discord
You can support this channel by buying the book through this link: https://amzn.to/2Z8xEpX
You can also support the channel by donating to / realphysics . Any amount will greatly help and is very much appreciated.
The textbook I am using is: Schroeder, Daniel V. "An Introduction to Thermal Physics" 1st ed., Addison Wesley Longman, 2005.