Tracert (Traceroute) windows Basic Networking Commands Tutorial Part-6 {2021}
Tracert (Traceroute) windows Basic Networking Commands Tutorial Part-6 {2021}
#windows #networking #Tracert #Traceroute #windows_networking
#windows_network_troubleshooting
Please subscribe our channel
Also like, share, comment
Stay tuned for new updates
✔ SYSTEMINFO AND HOSTNAME part -1 : • SYSTEMINFO AND HOSTNAME windows Basic...
✔ ipconfig part - 2 : • ipconfig windows Basic Networking Co...
✔ dns flush part - 3 : • dns flush windows Basic Networking C...
✔ Ping (part-1) part - 4 : • Ping (part-1) windows Basic Networki...
✔ Ping (part-2) part - 5 : • Ping (part-2) windows Basic Networki...
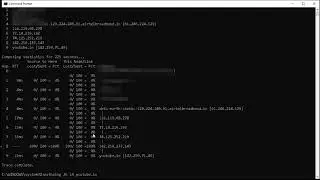
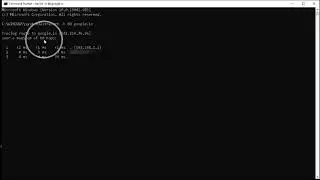
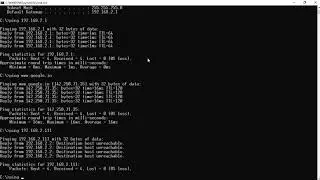
This is a basic tutorial to Displays TRACERT (Trace Route), a command-line utility that you can use to trace the path that an Internet Protocol (IP) packet takes to its destination.
How to Use the TRACERT Utility
The TRACERT diagnostic utility determines the route to a destination by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets to the destination. In these packets, TRACERT uses varying IP Time-To-Live (TTL) values. Because each router along the path is required to decrement the packet's TTL by at least 1 before forwarding the packet, the TTL is effectively a hop counter. When the TTL on a packet reaches zero (0), the router sends an ICMP "Time Exceeded" message back to the source computer.
TRACERT sends the first echo packet with a TTL of 1 and increments the TTL by 1 on each subsequent transmission, until the destination responds or until the maximum TTL is reached. The ICMP "Time Exceeded" messages that intermediate routers send back show the route. Note however that some routers silently drop packets that have expired TTLs, and these packets are invisible to TRACERT.
TRACERT prints out an ordered list of the intermediate routers that return ICMP "Time Exceeded" messages. Using the -d option with the tracert command instructs TRACERT not to perform a DNS lookup on each IP address, so that TRACERT reports the IP address of the near-side interface of the routers.
Tracert –d: - Specifies to not resolve addresses to host names
Tracert – h( maximum hops): - Specifies the maximum number of hops to search for the target
Tracert –4: - This option forces tracert to use IPv4 only.
Thanks for watching
Please subscribe our channel