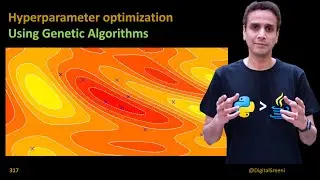
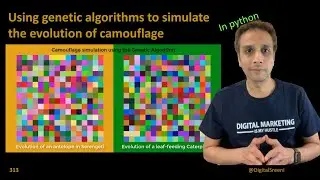
312 - What are genetic algorithms?
Genetic Algorithms (GA) are a type of evolutionary algorithm inspired by the process of natural selection in biological evolution.
They can be used to solve optimization problems, including finding the optimal values for various parameters.
GAs involve creating a population of candidate solutions, which are then evolved through the application of selection, crossover, and mutation operators.
The fittest individuals from each generation are selected to create the next generation, creating a process of natural selection over multiple generations.
GAs involve the application of selection, crossover, and mutation operators to create the next generation of individuals.
The selection operator involves selecting the fittest individuals from the current generation to create the next generation.
The crossover operator involves combining the genetic material of two individuals to create a new individual.
The mutation operator involves randomly changing the genetic material of an individual to introduce new variations in the population.
GAs have been successfully applied to various optimization problems, including finding the optimal values for various parameters in machine learning models.
They have also been used for feature selection, where the algorithm selects the best set of features for a particular task.
Other applications of GAs include optimization of engineering designs, scheduling problems, and financial forecasting.


![Прохождение Dungeon Siege 3 - [#6] Поместье Гундериков, часть 2 (на русском языке)](https://images.mixrolikus.cc/video/Z5YnzfpcR8o)

![84. [pro:]TEST! LIVE! - Selenide: automate with pleasure! with Andrei Solntsev](https://images.mixrolikus.cc/video/1d-nKyeTH2Y)