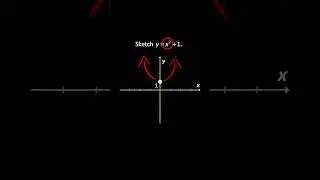
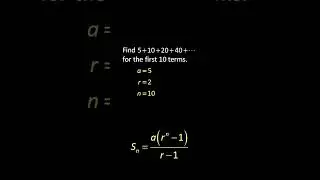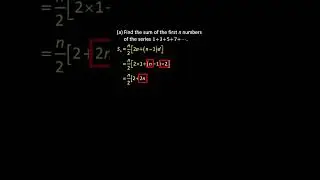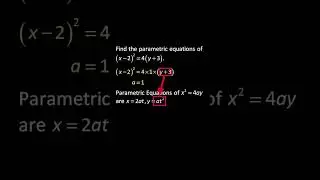√ The Photoelectric Cells Explained in Detail with Clear Examples. Watch this video to find out!
📢 Receive Comprehensive Mathematics Practice Papers Weekly for FREE 😊
Click this link to get: ▶️▶️▶️ https://iitutor.com/email-list/ ◀️◀️◀️
Photoelectric Cells. A photovoltaic cell is a photoelectric circuit that produces a photocurrent when struck by photons. These devices can be used to measure light intensity. They may also be used to charge capacitors or batteries. The efficiency of a photovoltaic cell is measured as a percentage. It shows how much light energy is converted into electrical energy. Most cells have an efficiency of 12–18%. The best solar cells have an efficiency of over 40%.
In the past, photovoltaic cells were constructed in vacuum tubes called photocells. Today, photovoltaic cells use semiconductors like silicon and gallium arsenide for electron emission. They respond best to ultraviolet light. Cameras and photographers use photocells to measure ambient light intensity. This lets them determine the correct camera exposure. Today, most cameras set the exposure automatically. Some professional photographers prefer to set exposure manually.
In a burglar alarm, UV light is beamed to a photocell. The resulting photocurrent energises an electromagnet. The electromagnetic holds a switch open. When the light is blocked, the magnet turns off and the circuit is completed, activating an alarm. In breathalysers, UV light is beamed through a potassium dichromate solution. Alcohol vapour causes the solution to change colour. A photocell can detect this colour change. When a user blows into the device, it can estimate the user’s blood alcohol level.
Solar cells convert solar energy to electrical energy. They consist of two plates sandwiched together, each containing a different type of semiconductor. This is called a p-n junction. The electrons in the cell are excited by ultraviolet photons from the Sun. The p-n junction limits the photoelectron flow to one direction (from n to p). The flow of the photoelectrons creates a voltage between the two plates. This voltage can be used to power electrical devices.




![mafia??? [gta in desc]](https://images.mixrolikus.cc/video/-YRyqGv_Bfs)