Binary file IO in python where to start
Download this code from https://codegive.com
In Python, you can work with binary files to read and write data that is not in text format. Binary files can store a wide variety of data, such as images, audio, video, and any other type of non-textual information. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to perform Binary File I/O in Python, including reading and writing binary files.
Before working with binary files, you should have a basic understanding of Python and file operations. If you are new to file I/O in Python, you might want to start with the basics of text file I/O and then proceed to binary file I/O. We'll assume you already have Python installed on your system.
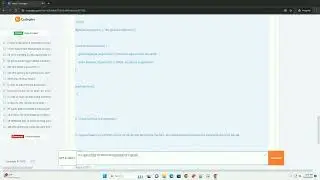
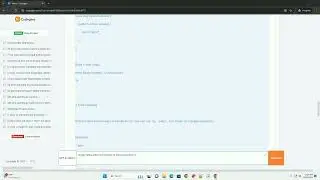
Let's start by creating a simple binary file that contains some data. In this example, we'll create a binary file with the following data: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
In the code above:
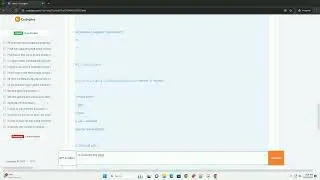
Now that we have a binary file, let's read its contents.
In the code above:
When you run this code, you will see the binary data as a series of bytes. In our case, it will be something like: bytearray(b'\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05').
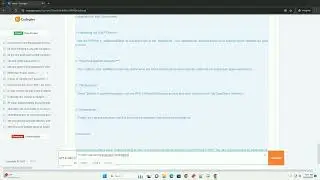
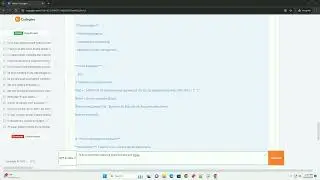
You can also write binary data incrementally by specifying a chunk of data to write at a time. This can be useful when working with large binary files.
In this example, we first write the data [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and then append [6, 7, 8, 9, 10] to the same binary file.
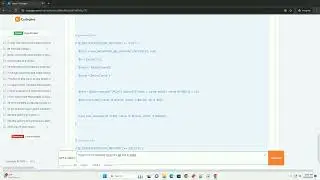
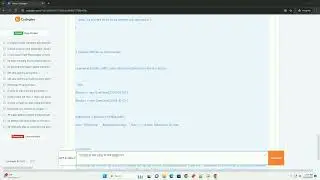
Reading binary data incrementally is similar to writing it. You can read data in chunks by specifying the number of bytes you want to read at a time.
In this example, we read the binary data in chunks of 2 bytes at a time until there's no more data to read.
Binary File I/O in Python allows you to work with non-textual data efficiently. You can create, read, write, and manipulate binary files using the techniques described in this tutorial. Make sure to close the file after you've finished working with it to free up system resources. Binary file I/O is essential for tasks like image processing, audio manipulation, and more.
ChatGPT
Binary file input and output (I/O) in Python allows you to work with non-text files, such as images, audio, video, and other binary data. Unlike text files, binary files store data in a format that isn't human-readable. In this tutorial, we'll explore how to perform binary file I/O in Python, covering the basics and providing code examples.
To work with binary files, you use the built-in open() function, just like with text files. However, you need to specify the mode as 'rb' for reading binary or 'wb' for writing binary. Here's how you can open a binary