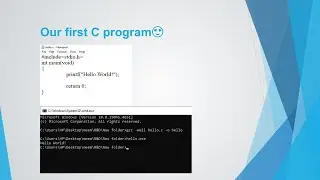
Basic Configuration of Cisco ASA Firewall || All easy explanation in Bangla✨
#cisco #ccna #CCNALAB
Description:-
A firewall is a network security device or software that is designed to monitor, filter, and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. The primary purpose of a firewall is to establish a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the Internet.
Here's a brief explanation of how a firewall works:
Packet Filtering:
Firewalls operate at the network level by examining data packets and making decisions based on predefined rules. Each data packet contains information such as source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and the protocol being used (TCP, UDP, etc.).
Rule-Based Decision Making:
Firewalls use a set of rules to determine whether to allow or block a packet. These rules are created by network administrators and define the criteria for filtering traffic. For example, a rule might allow incoming traffic on a specific port while blocking traffic on other ports.
Stateful Inspection:
Stateful inspection, also known as dynamic packet filtering, is a more advanced firewall technique. It keeps track of the state of active connections and makes decisions based on the context of the traffic. This allows firewalls to understand the state of a connection (such as whether it's part of an established session) and make more informed decisions.
Proxying and Network Address Translation (NAT):
Firewalls can act as intermediaries between internal and external systems. Proxy servers, for example, can receive requests from internal users, forward those requests to external servers on behalf of the users, and then relay the responses back. Network Address Translation (NAT) is another technique where a firewall rewrites the source or destination IP addresses of packets to hide the internal network structure.
Application Layer Filtering:
Some firewalls operate at the application layer and can inspect the content of the data packets to make decisions based on the specific applications or services being used. This allows for more granular control over the types of traffic that are allowed or blocked.

![[FREE] SLIMESITO x BEEZYB TYPE BEAT 2022 -](https://images.mixrolikus.cc/video/1EoTITwenvE)