BGP Basics Concept
ENARSI (300-410) BGP (BORDER GATEWAY PROTOCOL)
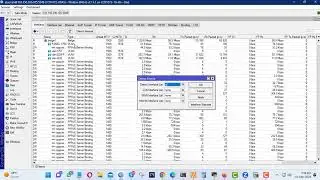
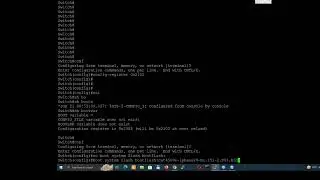
Border Gateway Protocol
RFC 1654 defines Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) as an EGP standardized path-vector routing protocol that provides scalability, flexibility, and network stability. When BGP was created, the primary design consideration was for IPv4 inter-organization connectivity on public networks, such as the Internet, or private dedicated networks. BGP is the only protocol used to exchange networks on the Internet, which has more than 600,000 IPv4 routes and continues to grow. BGP does not advertise incremental updates or refresh network advertisements like OSPF or ISIS. BGP prefers stability within the network, because a link flap could result in route computation for thousands of routes.
From the perspective of BGP, an autonomous system (AS) is a collection of routers under a single organization’s control, using one or more IGPs, and common metrics to route packets within the AS. If multiple IGPs or metrics are used within an AS, the AS must appear consistent to external ASs in routing policy. An IGP is not required within an AS, and could use BGP as the only routing protocol in it, too.
Autonomous System Numbers
Organizations requiring connectivity to the Internet must obtain an Autonomous System Number (ASN). ASNs were originally 2 bytes (16 bit) providing 65,535 ASNs. Due to exhaustion, RFC 4893 expands the ASN field to accommodate 4 bytes (32 bit). This allows for 4,294,967,295 unique ASNs, providing quite a leap from the original 65,535 ASNs.
Two blocks of private ASNs are available for any organization to use as long as they are never exchanged publicly on the Internet. ASNs 64,512–65,535 are private ASNs within the 16-bit ASN range, and 4,200,000,000–4,294,967,294 are private ASNs within the extended 32-bit range.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is responsible for assigning all public ASNs to ensure that they are globally unique. IANA requires the following items when requesting a public ASN:
Proof of a publicly allocated network range
Proof that Internet connectivity is provided through multiple connections
Need for a unique route policy from your providers






![💖Korean Drama💖Kiss Goblin [키스요괴]💖Ban Sook X Oh Yeon Ah💖Love Story FMV](https://images.mixrolikus.cc/video/vOGrHlW1SiE)